- Have any questions?
- 911 12345 29
- info@asianneurocentre.com
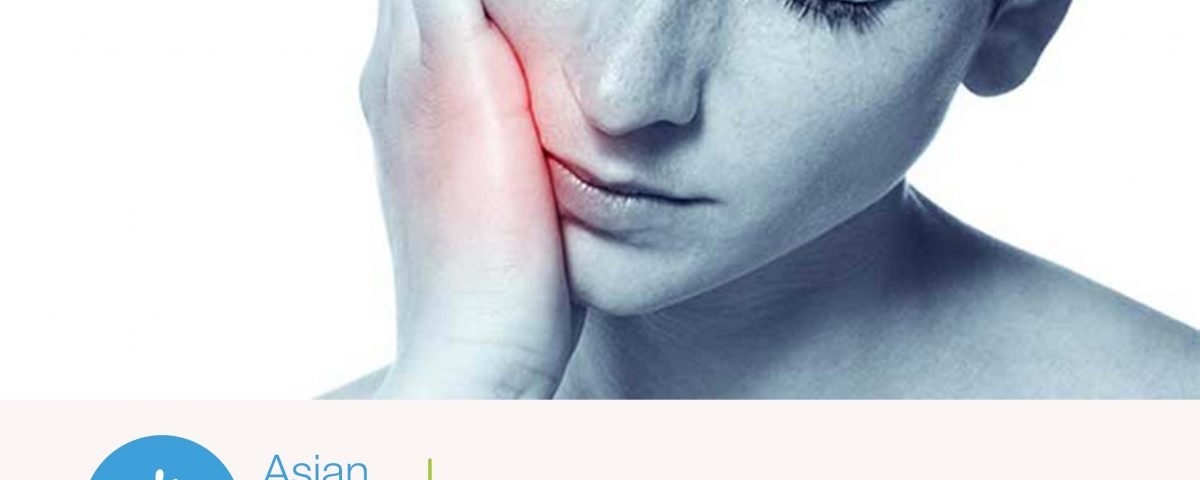
Trigeminal Neuralgia : a Stabbing and Boring Pain

Thank You For Your Trust, Support & Kindness, celebrating six years of my practice as Neurologist.
July 31, 2019
Sciatica –A Myth
September 9, 2019Trigeminal Neuralgia: a Stabbing and Boring Pain
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is one of the most painful and disabling of all medical conditions. Despite its dreadful symptom ofstabbing ,lancinating shock-like facial pain, trigeminal neuralgia is highly treatable. Howeverlancinating, the disease must be carefully differentiated from other causes of facial pain, and the correct treatment protocol must be applied in the case of a given patient.
What is trigeminal neuralgia (TN)?
Trigeminal neuralgia is inflammation of the fifth cranial nerve trigeminal nerve, causing intense,sharp, shooting cutting type facial pain. It is also known as tic douloureax because the intense pain can cause patients to contort their face into a grimace and cause the head to move away from the pain. The obvious movement is known as a tic.
The pain of trigeminal neuralgia is so intense and may be an isolated episode or may be occur repeatedly every few hours, minutes, or seconds. There can be period of remission of months or years between attacks, but in some patients whose pain is not well controlled; it can lead to a disabling chronic pain syndrome, affecting activities of daily life and cause depression.
Though it can affect people of any age, trigeminal neuralgia tends to afflictadult people older than30 years of age. It affects the right side of the face five times more often than the left cause unknown.

Trigeminal Neuralgia
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
Most often, the cause of trigeminal neuralgia is idiopathic or primary , meaning the cause is not known. However, a hypothesis of demyelination of nerve at its root is proposed for idiopathic causes. There are some instances when the nerve can be compressed by nearby blood vessels, aneurysms, or tumor called as secondary trigeminal neuralgia.
There are various other inflammatory causes of trigeminal neuralgia because of systemic diseases including multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and Lyme disease. There also is an association with collagen vascular diseases including scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus.
What are the symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia?
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia include an acute onset of sharp, shooting , cutting ,stabbing pain to one side of the face. It mostly begin at the angle of the jaw and radiate along the junction lines; between the ophthalmic branchV1 and maxillary branch V2, or the maxillary branch V2 and the mandibular branch V3,involving area between nose and mouth.
The pain is very severe and described as an electric shock. It may be made worse by light touch (TRIGGER) chewing, or cold exposure in the mouth, hall mark feature. In the midst of an attack, affected individuals shield their face trying to protect it from being touched. This is an important diagnostic sign because with many other pain syndromes like a toothache, the person will rub or hold the face to ease the pain.
Initially there may be only one episode or attack of facial pain, the person may experience recurrent episodes of sharp pain every few minutes , hours or every few seconds. Between the attacks, the pain resolves completely and the person is asymptomatic. However, because fear of recurrence of intense pain might return, people can be quite distraught. Trigeminal neuralgia tends not to occur when the person is asleep, and this differentiates it from migraines, which often waken the person.
After the first episode of attacks, the pain may subside or remits for months or years but there is always the risk that trigeminal neuralgia will recur without warning.
How is trigeminal neuralgia diagnosed?
Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia is a clinical diagnosis and often no testing is required after the health care professional takes a history of the situation and performs a physical examination which should be normal. However MRI brain with neuralgia protocol is done to rule out any compression by any vassels or tumor.It is important to remember that the neurologic exam must be normal.
The International Headache Society has established criteria for making the diagnosis and includes the following:
Paroxysmal attacks of pain lasting from a fraction of a second to 2 minutes, affecting 1 or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve and fulfilling criteria B and C.
Pain has at least one of the following characteristics: (1) intense, sharp, superficial or stabbing; or (2) precipitated from trigger areas or by trigger factors
Attacks stereotyped in the individual patient
No clinically evident neurologic deficit
Not attributed to another disorder
What is the treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia most often is treated with good success using a single anticonvulsant medication such as carbamazepine (Tegretol).Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gabarone), baclofen and phenytoin (Dilantin, Dilantin-125) may be used as second line drugs, often in addition to carbamazepine. In many patients, as time progresses, carbamazepine becomes less effective and these drugs can be used in combination to control the pain.Lamotrigine (Lamictal) may be prescribed for multiple sclerosis patients who develop trigeminal neuralgia.
Now a daysinj Botox is given for relief in pain, but this procedure is temporary and pain use to reappear after 4 to 6 months.
Microvasculardecompression.Brain stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma knife).,Glycerol injection , Balloon compression,Radiofrequency thermal lesioning are other treatment options
If you live in Indore and surrounding areas and looking for the best Neuro centre in Indore to find out how you can improve your neurological disorder, you don’t have to look beyond Asian Neuro Centre. It is by far the best Neuro Centre in Indore. Book an appointment to discuss your neurological problem with our expert advisors.

